Trochanteric bursitis exercises, benefits, and diet tips to reduce pain and improve mobility. Get expert advice for faster recovery and prevention.
Introduction
Trochanteric Bursitis Exercises is a painful condition that affects the hip and outer thigh area, causing discomfort and limiting mobility. Whether you’re dealing with it personally or helping someone else manage the condition, understanding the role of exercises in recovery is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about trochanteric bursitis exercises, their benefits, a diet plan to complement your healing process, and how simple lifestyle changes can help you heal faster. Let’s dive in!
What is Trochanteric Bursitis? [1]
Trochanteric bursitis occurs when the bursa—the small, fluid-filled sacs located near the outer part of your hip—becomes inflamed. The bursa acts as a cushion between bones and soft tissues, allowing smooth movement of the joint. When it becomes irritated, it can cause pain and swelling in the outer hip region, which can be exacerbated by certain movements or prolonged pressure on the hip.
Causes of Trochanteric Bursitis

There are several factors that contribute to the development of trochanteric bursitis, including:
- Overuse or repetitive movement: Activities that require repetitive hip motion, such as running or cycling, can strain the bursa.
- Injury or trauma: A fall or impact to the hip may result in bursitis.
- Age and wear: As we age, the tissues around the hip joint can become less flexible and more prone to irritation.
- Abnormal posture or gait: Misalignments in the hips or legs can place additional stress on the bursa, contributing to inflammation.
Symptoms of Trochanteric Bursitis
The most common symptom of trochanteric bursitis is pain in the outer hip, which may radiate down the outer thigh. This pain may worsen during certain activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or lying on the affected side. Other symptoms include:
- Swelling or tenderness over the hip.
- Stiffness or a reduced range of motion in the hip joint.
- Pain that increases at night or after prolonged standing.
How to Identify Trochanteric Bursitis
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. A physical exam and possibly an X-ray or MRI may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions, such as hip arthritis.
Exercises for Trochanteric Bursitis
When dealing with trochanteric bursitis, exercises play a vital role in reducing pain, increasing mobility, and strengthening the muscles around the hip to prevent future flare-ups. However, it’s essential to focus on gentle exercises that target both flexibility and strength.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching helps to increase flexibility, improve joint movement, and reduce muscle tension around the hip. Here are two effective stretches:
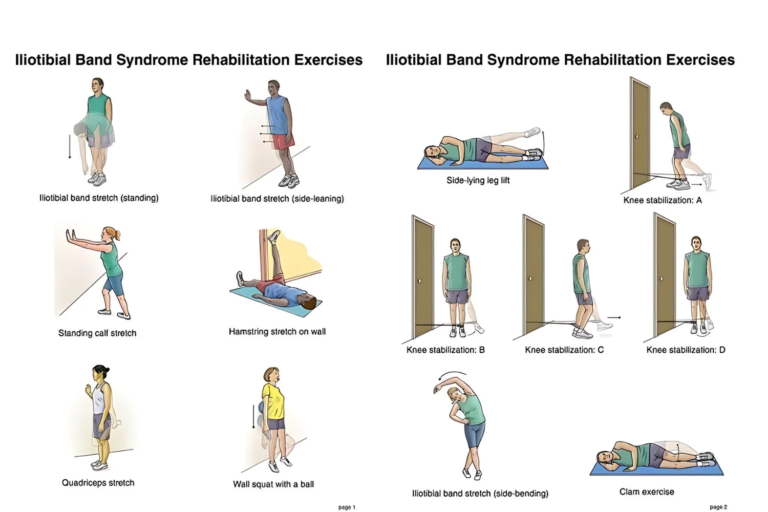
IT Band Stretch
The iliotibial (IT) band runs along the outer side of your thigh and connects to your hip. Tightness in the IT band can exacerbate bursitis. Here’s how to stretch it:
- Stand with your feet together, then cross one leg behind the other.
- Lean your torso toward the side of the back leg while keeping your torso upright.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds and repeat on the other side.
Hip Flexor Stretch
Tight hip flexors can contribute to pain in the hip and worsen bursitis. To stretch the hip flexors:
- Step forward into a lunge position, ensuring your back leg is straight and your hips face forward.
- Lower your hips toward the floor, keeping your torso upright.
- Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds, then switch sides.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the muscles surrounding the hip joint is essential for providing support and reducing pressure on the bursa. Here are a few exercises to try:
Glute Bridges
This exercise targets your glutes, lower back, and core muscles, which are important for stabilizing the hip joint.
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
- Lift your hips toward the ceiling, squeezing your glutes.
- Hold for a few seconds, then lower your hips slowly back to the starting position.
- Perform 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
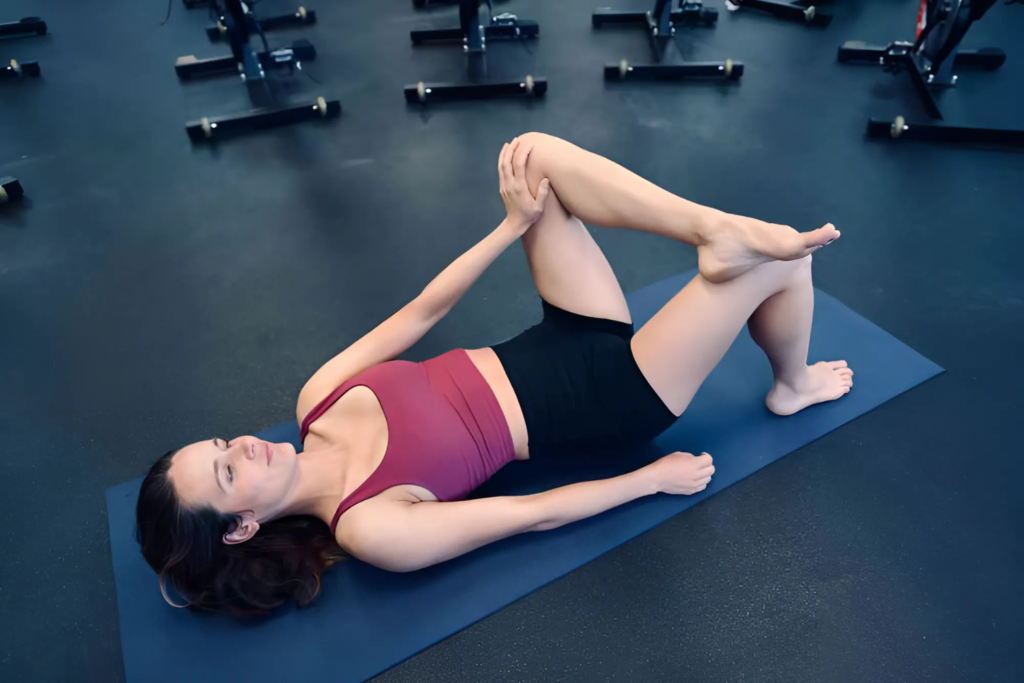
Clamshell Exercise
Clamshells work the hip abductors, which help stabilize the hip and prevent further irritation of the bursa.
- Lie on your side with your knees bent at a 45-degree angle and your feet stacked on top of each other.
- Keeping your feet together, lift your top knee toward the ceiling while keeping your pelvis stable.
- Lower your knee back to the starting position and repeat for 10-15 reps on each side.
Low-Impact Cardio Exercises
While high-impact exercises may worsen symptoms, low-impact cardio activities can help you stay active without putting additional strain on your hip.
Swimming
Swimming is an excellent exercise for people with trochanteric bursitis, as it allows for full-body movement while being gentle on the joints. The water’s buoyancy supports your body, reducing pressure on your hips.
Cycling
Cycling, particularly on a stationary bike, is another low-impact exercise that can strengthen the muscles around the hip without causing additional stress on the joint. Just be sure to adjust the bike to a comfortable height to avoid overstretching or straining your hip.
Benefits of Trochanteric Bursitis Exercises
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Pain Reduction | Regular exercises help reduce inflammation around the hip joint, which can alleviate the sharp pain and tenderness caused by trochanteric bursitis. Stretching and strengthening the muscles around the hip can provide long-term relief. |
| Improved Flexibility | Stretching exercises improve flexibility in the hip joint and surrounding muscles, enhancing the range of motion and making it easier to perform daily tasks like walking, sitting, and climbing stairs without discomfort. |
| Muscle Strengthening | Strengthening exercises, such as glute bridges and clamshells, target muscles around the hip, such as the glutes, hip flexors, and abductors. Stronger muscles help stabilize the hip joint and reduce stress on the bursa. |
| Enhanced Mobility | By strengthening and stretching the muscles, exercises improve overall hip function. This allows individuals to move more freely and perform activities like walking, bending, or squatting without aggravating the bursitis. |
| Prevention of Future Flare-Ups | Consistent exercise helps prevent future episodes of bursitis by maintaining muscle strength, joint mobility, and proper posture, which reduces the chances of re-injury and irritation to the bursa. |
| Reduced Swelling and Inflammation | Low-impact exercises increase blood circulation to the affected area, helping to flush out inflammatory chemicals and promote healing. This leads to reduced swelling and quicker recovery from flare-ups. |
| Improved Posture and Alignment | Certain exercises, such as IT band stretches, improve posture and joint alignment, which reduces the stress placed on the hip, preventing further irritation of the bursa and improving overall body mechanics. |
| Better Joint Health | Regular movement helps maintain the health of the hip joint and surrounding soft tissues by keeping them flexible and strong. This can help avoid long-term issues like arthritis or joint degeneration. |
| Increased Blood Flow | Exercise stimulates blood circulation, which aids in faster delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the hip joint, speeding up the healing process and reducing stiffness. |
| Boosted Confidence | As individuals see improvements in mobility and pain reduction, it boosts confidence and encourages them to engage in more physical activities, leading to a more active and healthy lifestyle overall. |
| Low-Risk, Low-Impact Relief | Many recommended exercises, such as swimming and cycling, are low-impact, meaning they won’t put added pressure on the hip while still helping to strengthen and rehabilitate the joint. These exercises can be performed safely over time. |
| Mental Well-being | Exercise is known to improve mood and reduce stress. The positive effects on mental health can provide a sense of control over the condition and motivate individuals to continue their rehabilitation efforts. |
Pain Reduction
Exercise helps to reduce inflammation around the hip and improves blood circulation, which can relieve pain and promote healing over time.
Improved Mobility
Strengthening and stretching exercises improve flexibility and range of motion, allowing for better movement of the hip joint. This makes daily activities, such as walking or climbing stairs, easier to perform.
Prevention of Future Flare-Ups
Regular exercise helps to maintain the strength and flexibility of the muscles around the hip, preventing future episodes of bursitis and promoting overall joint health.
Diet Plan for Trochanteric Bursitis
Nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting the healing process. A balanced, anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce the pain and swelling associated with bursitis.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Certain foods are known to help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Here are some foods to include in your diet:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as walnuts and flaxseeds, omega-3s reduce inflammation in the body.
- Turmeric and Ginger: Both of these spices have natural anti-inflammatory properties. You can incorporate them into your meals or drink them as teas.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and other leafy vegetables are packed with antioxidants that help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
These fatty acids are essential for joint health and help fight inflammation. Aim to include fatty fish in your meals at least 2-3 times a week, or consider a supplement if you’re not a fan of fish.
Turmeric and Ginger
Curcumin, found in turmeric, and gingerol, found in ginger, are both potent anti-inflammatory compounds. Add turmeric to curries, soups, or smoothies for a health boost, or sip on ginger tea.
Foods to Avoid
While some foods can help reduce inflammation, others can exacerbate it. These include:
- Processed Foods: Foods high in trans fats and refined sugars can worsen inflammation and slow down recovery.
- Excessive Sugar: Consuming too much sugar can increase inflammatory markers in the body.
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread, pasta, and other refined carbs can also contribute to inflammation and slow healing.
Celeries and Bursitis: A Helpful Addition to Your Diet
Celery may not be the first food that comes to mind for joint health, but it has a lot to offer. Celery contains flavonoids and antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
Celery’s Nutritional Profile
Celery is low in calories and a good source of vitamins like Vitamin K and Folate. It also contains fiber, which supports digestive health. These nutrients can help improve overall well-being and assist in the healing process.
Celery and Inflammation
Celery has been shown to have natural anti-inflammatory properties, making it a great food to include in your diet when managing bursitis. You can consume it in salads, soups, or even enjoy celery juice for an added anti-inflammatory boost.
Celery Juice for Healing
Drinking celery juice regularly is becoming a popular remedy for reducing inflammation and promoting overall health. Though more research is needed, it’s worth considering as part of your anti-inflammatory diet.
Conclusion
Trochanteric bursitis can be a painful condition, but with the right combination of exercises and dietary changes, it’s possible to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Regular stretching, strengthening exercises, and anti-inflammatory foods can all play a pivotal role in your recovery journey. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise program or diet to ensure the best approach for your specific condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best exercise for trochanteric bursitis?
Gentle stretching exercises, such as IT band stretches and hip flexor stretches, combined with strengthening exercises like glute bridges and clamshells, are ideal.
Can I exercise with trochanteric bursitis?
Yes, gentle and low-impact exercises can help relieve pain and improve mobility.
How long does it take to recover from trochanteric bursitis?
Recovery time varies, but with the right exercises and diet, many people feel relief within a few weeks to months.
Is swimming good for trochanteric bursitis?
Yes, swimming is an excellent low-impact exercise that allows you to strengthen muscles without putting additional strain on the hip.
What foods should I avoid with trochanteric bursitis?
Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar, and refined carbohydrates, which can worsen inflammation and slow recovery.
Can diet impact trochanteric bursitis?
Yes, an anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce swelling and promote healing. Include omega-3s, turmeric, ginger, and leafy greens.
How often should I do exercises for bursitis?
Aim for 3-4 sessions per week, focusing on stretching and strengthening exercises to improve hip function.
Can I use ice or heat for trochanteric bursitis pain?
Ice can help reduce inflammation, while heat can relax muscles. Use both as needed based on your symptoms.
What should I do if my trochanteric bursitis flares up?
Rest and apply ice to the affected area. Avoid activities that exacerbate the pain, and consult with your doctor if symptoms persist.
When should I see a doctor for trochanteric bursitis?
If symptoms persist or worsen despite self-care, consult a doctor for further evaluation and treatment options
By healthylyfe