Learn how lunges boost muscle growth and strength. This simple exercise targets your legs, glutes, and core while improving balance and fitness.
Introduction
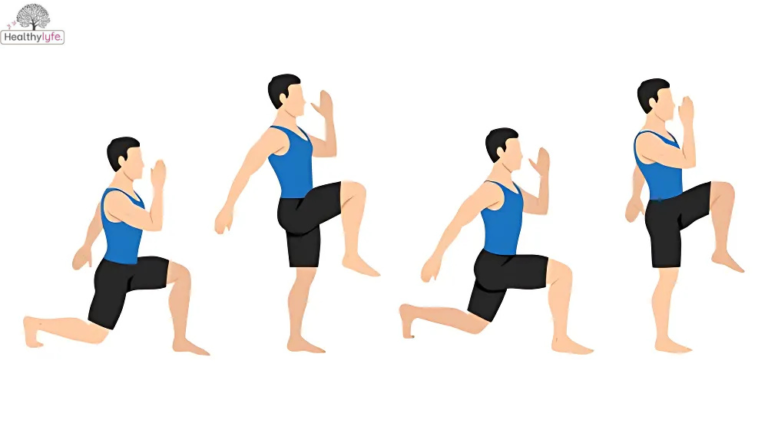
Lunges are one of the best exercises to build muscle and improve strength. They target your legs, glutes, and core while also helping with balance and flexibility. Whether you’re just starting your fitness journey or you’re a seasoned athlete, lunges are a simple yet effective way to boost your lower body strength. In this article, we’ll explain why lunges are great, how they work, and how to add them to your workouts for the best results.
What is Lunges?
Lunges are a popular lower-body exercise that strengthens your legs, glutes, and core. They involve stepping forward, backward, or sideways with one leg while bending your knees to lower your body. This movement works multiple muscle groups, improves balance, and enhances flexibility.
Lunges are versatile and can be done anywhere, with or without weights. They are ideal for building muscle, improving athletic performance, and even enhancing everyday movements like walking or climbing stairs. There are many variations, such as forward lunges, reverse lunges, and side lunges, making it easy to adapt them to your fitness level and goals.
Type of Lunges Exercise
Lunges come in various forms, each targeting specific muscle groups and serving different fitness goals. Here are some of the most common types:

Forward Lunges
- How to Do It: Step forward with one leg, lower your body until both knees are bent at 90 degrees, and then push back to the starting position.
- Benefits: Strengthens quads, glutes, and hamstrings while improving balance.
Reverse Lunges
- How to Do It: Step backward with one leg, lower your body into a lunge position, and return to standing.
- Benefits: Easier on the knees than forward lunges; targets glutes and hamstrings more intensely.
Walking Lunges
- How to Do It: Perform a lunge, but instead of returning to the starting position, step forward with the other leg. Repeat as you move forward.
- Benefits: Great for functional strength, coordination, and endurance.
Side Lunges (Lateral Lunges)
- How to Do It: Step out to the side with one leg, bend the knee, and lower your body while keeping the other leg straight.
- Benefits: Targets inner thighs, glutes, and improves lateral mobility.
Curtsy Lunges
- How to Do It: Step one leg diagonally behind the other and lower your body into a lunge position.
- Benefits: Strengthens glutes, quads, and improves hip stability.
Jump Lunges
- How to Do It: Perform a lunge, then explosively jump and switch legs mid-air.
- Benefits: Builds power, endurance, and burns calories.
Split Squat (Stationary Lunge)
- How to Do It: Position one foot forward and the other back, then lower and raise your body without stepping.
- Benefits: Targets quads, glutes, and hamstrings with greater stability.
Overhead Lunges
- How to Do It: Perform a lunge while holding weights or a barbell overhead.
- Benefits: Enhances core stability, shoulder strength, and balance.
Walking Lunges with Rotation
- How to Do It: Hold a weight at chest level, perform a walking lunge, and rotate your torso toward the leading leg.
- Benefits: Engages the core and improves rotational strength.
Bulgarian Split Squats
- How to Do It: Place one foot on a bench behind you and perform a lunge with the other leg.
- Benefits: Intensifies glute and quad activation.
Benefits of Lunges Exercise [1]
Lunges are a powerful exercise with numerous benefits for strength, flexibility, and overall fitness. Whether you’re aiming to build muscle, improve balance, or enhance athletic performance, lunges are a versatile addition to any workout routine. Here’s a detailed look at the key benefits of lunges:
Builds Lower Body Strength
Lunges target major muscle groups in your lower body, including:
- Quadriceps
- Hamstrings
- Glutes
- Calves
By engaging these muscles, lunges help you develop strength and power, which can improve your performance in sports and everyday activities.
Improves Balance and Stability
Performing lunges requires core activation and stability to maintain proper form. This helps improve your balance and coordination over time. Enhanced stability also reduces the risk of falls and injuries.
Enhances Core Strength
Lunges engage your core muscles as you stabilize your body during the movement. A stronger core contributes to better posture, reduced back pain, and improved overall strength.
Boosts Flexibility and Mobility
The dynamic movement of lunges stretches and strengthens your hip flexors, hamstrings, and calves. This leads to better flexibility and mobility, which are essential for pain-free movement and athletic performance.
Corrects Muscle Imbalances
Lunges are a unilateral exercise, meaning they work one side of your body at a time. This helps identify and address strength imbalances between your legs, leading to improved symmetry and overall functionality.
Increases Functional Fitness
Lunges mimic natural movements, such as walking and climbing stairs, making them a functional exercise. They strengthen the muscles and patterns you use in daily life, enhancing your overall physical ability.
Supports Weight Loss
Lunges are a compound exercise that burns calories by working multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Adding weights or doing high-intensity lunge variations like jump lunges can further increase calorie burn.
Versatile and Easy to Modify
Lunges can be performed anywhere, without the need for equipment. There are numerous variations to suit any fitness level, from beginners to advanced athletes.
Reduces Risk of Injury
By strengthening your lower body and improving balance and flexibility, lunges help protect your joints, ligaments, and tendons from injuries.
Promotes Better Posture
The upright posture required during lunges strengthens your back and core, leading to improved posture over time.
Diet Plan for Lunges Exercise
To get the most out of lunges and maximize muscle growth, strength, and recovery, a well-balanced diet is essential. Your diet should provide enough energy for your workouts, support muscle repair, and enhance overall performance. A combination of proteins, carbohydrates, healthy fats, and hydration is key to fueling your body effectively.
| Meal | Time | What to Include | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Workout | 30–60 minutes before exercise | – Oatmeal with banana and a scoop of peanut butter – Protein smoothie with whey and berries | Provides quick energy from carbs and protein for sustained performance. |
| Post-Workout | Within 30 minutes after exercise | – Grilled chicken breast or tofu – Brown rice or quinoa – Steamed vegetables | Supports muscle recovery and replenishes glycogen stores. |
| Breakfast | Morning | – Scrambled eggs with avocado – Whole-grain toast – Fresh fruit | Kickstarts metabolism and fuels muscles with protein and healthy fats. |
| Lunch | Midday | – Grilled salmon or lean beef – Sweet potatoes – Mixed greens with olive oil and nuts | Supplies essential nutrients for muscle repair and sustained energy. |
| Dinner | Evening | – Baked chicken or turkey – Roasted vegetables – Couscous or whole-grain pasta | Balances protein, carbs, and fiber to aid recovery and keep you full. |
| Snacks | Between meals | – Greek yogurt with honey – Handful of almonds – Rice cakes with almond butter | Prevents energy dips and supports muscle recovery throughout the day. |
| Hydration | Throughout the day | – At least 8–10 cups of water – Electrolyte-rich drinks (optional for intense workouts) | Keeps the body hydrated for optimal performance and recovery. |
Tips for Success
Lunges are a fantastic exercise for building strength, improving balance, and enhancing mobility. However, to maximize their benefits and avoid injury, it’s essential to perform them correctly and integrate them effectively into your workout routine. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced athlete, these tips can help you succeed with lunges.
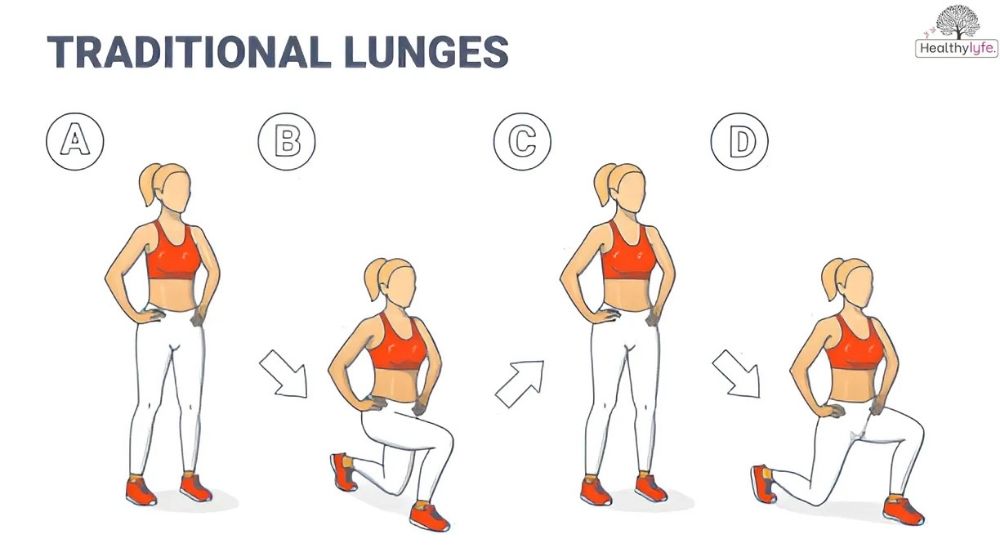
Master Proper Form
- Keep your upper body upright and core engaged throughout the movement.
- Step forward, backward, or sideways far enough to form a 90-degree angle at both knees.
- Avoid letting your front knee extend beyond your toes to protect your joints.
Start Without Weights
- Focus on mastering the basic lunge with body weight before adding resistance.
- This helps build a solid foundation of strength and stability.
Warm Up Before Lunges
- Perform dynamic stretches or light cardio to loosen up your muscles.
- Pay extra attention to warming up your hips, knees, and ankles for better mobility.
Gradually Increase Intensity
- Add weights (dumbbells, barbells, or kettlebells) once you’re comfortable with bodyweight lunges.
- Increase the number of repetitions or sets gradually to avoid overtraining.
Mix Up Variations
- Incorporate different lunge variations, such as forward lunges, reverse lunges, and side lunges, to target various muscle groups.
- This keeps your routine fresh and ensures balanced development.
Maintain a Consistent Pace
- Perform lunges slowly and with control to engage your muscles fully.
- Avoid rushing through the movement, which can compromise form and effectiveness.
Focus on Core Engagement
- Keep your core tight throughout the exercise to maintain balance and stability.
- This also protects your lower back and improves posture.
Pair Lunges with a Balanced Workout Plan
- Combine lunges with other strength, cardio, and flexibility exercises for a well-rounded fitness routine.
- This prevents overuse injuries and promotes overall fitness.
Rest and Recover
- Allow your muscles to recover by taking rest days or alternating lunges with other exercises.
- Proper recovery enhances performance and prevents fatigue.
Fuel Your Body
- Follow a balanced diet rich in protein, complex carbs, and healthy fats to support your workouts.
- Stay hydrated to keep your muscles functioning optimally.
Conclusion
Lunges are one of the best exercises to build strength, improve balance, and boost flexibility. They work multiple muscle groups and can easily be added to any workout, no matter your fitness level. By doing lunges regularly and using proper form, you can see great results in your strength, performance, and overall health. Paired with a balanced diet and rest, lunges can help you reach your fitness goals faster.
FAQs about Lunges Exercise
What are lunges?
Lunges are a strength-training exercise that targets the lower body, particularly the quadriceps, glutes, hamstrings, and calves. They involve stepping forward, backward, or to the side while lowering your body into a split-squat position.
What muscles do lunges work?
Lunges primarily target the quadriceps, glutes, hamstrings, and calves. They also engage the core for stability.
What are the benefits of doing lunges?
Lunges improve lower body strength, balance, coordination, hip flexibility, and core stability. They are also excellent for functional fitness and can enhance athletic performance.
What are the different types of lunges?
Common variations include:
Forward lunges
Reverse lunges
Walking lunges
Side (lateral) lunges
Curtsy lunges
Jump lunges
Stationary lunges
How do I perform a basic forward lunge?
Stand tall with feet hip-width apart.
Step forward with one leg.
Lower your hips until both knees are bent at 90 degrees.
Keep your front knee above your ankle and your back knee off the ground.
Push off the front foot to return to the starting position.
Should my knee touch the ground during a lunge?
Your back knee should hover just above the ground, not touch it, to avoid injury and maintain proper form.
How many lunges should I do?
Start with 2-3 sets of 10-15 reps per leg. Adjust based on your fitness level and goals.
Can lunges help tone my legs?
Yes, lunges are highly effective for toning and strengthening the muscles in your legs and glutes.
Are lunges good for weight loss?
Lunges can support weight loss when combined with a calorie-controlled diet and other exercises. They burn calories, build muscle, and improve metabolism.
What is the difference between lunges and squats?
Lunges are a unilateral exercise (working one leg at a time), while squats are bilateral (working both legs together). Lunges also require more balance and coordination.
How can I make lunges harder?
Add weights (dumbbells, kettlebells, or a barbell).
Perform jump lunges.
Increase the range of motion.
Slow down the movement.
Try walking lunges or multi-directional lunges.
What is the proper form for lunges?
Keep your chest upright.
Avoid letting your front knee go past your toes.
Keep your core engaged for balance.
Ensure equal weight distribution between both legs.
Can beginners do lunges?
Yes, beginners can start with stationary lunges or hold onto a stable surface for balance until they build strength and confidence.
What are common mistakes in lunges?
Letting the front knee go too far forward.
Leaning forward excessively.
Not keeping the back knee close to the ground.
Losing balance or rushing through the movement.
Are lunges bad for the knees?
When done with proper form, lunges are not bad for the knees. Poor form, such as improper knee alignment, can cause discomfort or injury.
Can I do lunges every day?
Yes, but it’s essential to listen to your body. Overworking the same muscles daily can lead to fatigue and hinder recovery. Incorporate rest or alternate exercises.
Are lunges better than squats?
Both exercises are excellent for the lower body. Lunges may be better for balance and single-leg strength, while squats are great for overall leg power and strength.
Can I do lunges if I have tight hips?
Yes, but start with a smaller range of motion and focus on hip stretches to improve flexibility over time.
What equipment can I use for lunges?
Dumbbells, kettlebells, barbells, resistance bands, and weighted vests can all be used to increase the intensity of lunges.
How do I avoid losing balance during lunges?
Focus on engaging your core, keep your eyes on a fixed point, and take smaller steps if needed. Over time, your balance will improve with practice.
By healthylyfe