Joint pain relief involves healthy habits, proper nutrition, and natural remedies to reduce discomfort and improve mobility.
Introduction
Living with joint pain can be a daily challenge, whether it stems from arthritis, an injury, or general wear and tear. While there may not always be a quick fix, adopting practical strategies can significantly improve your comfort and quality of life. From lifestyle adjustments and gentle exercises to dietary choices and mindfulness practices, these tips can help you manage discomfort and keep moving with ease.
Understanding Joint Pain
Joint pain is a common issue that affects people of all ages and activity levels. It can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain, impacting daily activities and overall well-being. Joints are the points where two or more bones meet, providing flexibility and support for movement. When these structures are affected by injury, inflammation, or wear and tear, it can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Common Causes of Joint Pain
Joint pain can result from various factors, ranging from temporary injuries to chronic conditions. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for effective management. Below are some of the most common causes of joint pain:
Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis: Often associated with aging, this degenerative condition occurs when the cartilage that cushions joints wears down, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the joint lining, causing inflammation, swelling, and pain.
Injuries
- Sprains or strains affecting the ligaments, tendons, or muscles around a joint.
- Fractures or dislocations that damage the joint structure.
- Post-traumatic arthritis resulting from a past injury.
Overuse and Repetitive Stress
- Repetitive movements or excessive physical activity can lead to overuse injuries, such as tendonitis or bursitis, causing inflammation around the joint.
Gout and Other Crystal Deposits
- Gout occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joint, often causing sudden and intense pain, redness, and swelling.
- Other conditions, like pseudogout, involve calcium crystal deposits in the joints.
Autoimmune Conditions
- Lupus, spondyloarthritis, and psoriatic arthritis are examples of autoimmune disorders that can cause chronic joint pain and inflammation.
Infections
- Septic arthritis occurs when a bacterial or viral infection invades the joint, leading to severe pain and swelling.
- Viral illnesses, such as the flu or Lyme disease, may also cause joint discomfort.
Age and Wear-and-Tear
- With aging, joints may naturally deteriorate, leading to stiffness and discomfort due to reduced cartilage and joint lubrication.
Other Health Conditions
- Conditions like fibromyalgia, hypothyroidism, and obesity can contribute to or exacerbate joint pain by increasing strain or sensitivity.
Symptoms to Watch For
Joint pain can present with various symptoms, depending on its cause. Paying attention to these signs can help you determine the severity of the issue and guide your next steps, including seeking medical advice.
Common Symptoms
- Pain or Discomfort: A persistent ache, sharp pain, or throbbing sensation in the joint.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the joint, which may feel warm to the touch.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the joint, especially after periods of inactivity or upon waking.
- Redness: Discoloration or warmth in the area surrounding the joint.
- Weakness or Instability: A feeling that the joint is giving way or lacks support.
Additional Symptoms to Note
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty bending, straightening, or rotating the joint fully.
- Grinding or Clicking Sounds: Unusual noises during joint movement, often due to cartilage damage.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations that may indicate nerve involvement.
- Fatigue or Fever: Generalized symptoms, particularly if joint pain is due to an infection or autoimmune condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention
- Pain persists for more than a few days without improvement.
- Joint swelling or redness worsens.
- You experience a sudden, intense onset of joint pain.
- Fever accompanies the pain, suggesting infection.
- The joint appears deformed or is immobilized after an injury.
Why Ignoring Joint Pain Can Be Harmful {1}
Ignoring joint pain can lead to more serious health issues and long-term complications. While mild discomfort may seem manageable at first, untreated or poorly managed joint pain can escalate, affecting mobility, quality of life, and overall health. Here’s why ignoring joint pain can be harmful:
Progression of Underlying Conditions
Many causes of joint pain, such as arthritis or injuries, can worsen over time if left untreated. For example, osteoarthritis can lead to more severe cartilage damage and joint deformity, making treatment less effective as the condition advances.
Increased Risk of Joint Damage
Ignoring joint pain may result in untreated inflammation or strain, which can cause further damage to the joint’s cartilage, ligaments, and surrounding tissues. Over time, this may result in permanent joint damage, leading to reduced function and mobility.
Loss of Mobility
Chronic joint pain can lead to decreased physical activity due to discomfort, resulting in weakened muscles and a reduced range of motion. This can make everyday activities, like walking, climbing stairs, or even simple tasks, increasingly difficult.
Mental and Emotional Impact
Chronic joint pain can significantly impact mental health, leading to anxiety, depression, and frustration due to limited physical capabilities. The discomfort and inability to perform daily activities can create a sense of isolation and affect overall well-being.
Increased Risk of Secondary Complications
Neglecting joint pain can lead to other related issues such as poor posture, gait changes, or compensatory strain on other joints, increasing the risk of injury or strain elsewhere in the body.
Delayed Treatment and Recovery
Early intervention is crucial for managing joint pain effectively. Ignoring symptoms may delay treatment, making recovery more challenging and less successful. In some cases, early management can prevent the need for more invasive treatments like surgery.
Compromised Quality of Life
Long-term joint pain can hinder your ability to enjoy physical activities, social interactions, and hobbies, ultimately impacting your quality of life.
When to See a Doctor
Joint pain can vary in intensity and cause, so knowing when to seek medical attention is essential for effective management and treatment. Below are signs that indicate it’s time to consult a healthcare professional:
Persistent or Worsening Pain
If joint pain persists for more than a few days or becomes increasingly severe, it’s important to get it evaluated by a doctor.
Swelling or Redness
Persistent inflammation, swelling, or redness around the joint may indicate an underlying issue that requires medical attention.
Stiffness
Difficulty moving the joint, especially after prolonged periods of rest or inactivity, can signal a serious condition, such as arthritis or injury.
Loss of Functionality
If you experience a sudden inability to move or bear weight on the affected joint, it may require immediate medical evaluation.
Accompanying Symptoms
Fever, unexplained weight loss, or numbness/tingling alongside joint pain may indicate an underlying infection, autoimmune condition, or other serious health issue.
Injury or Trauma
If the joint pain results from a recent injury, such as a fall or accident, it’s important to consult a doctor to rule out fractures, dislocations, or ligament damage.
Chronic Conditions
If you have a known chronic condition like arthritis or gout, persistent flare-ups or a sudden increase in joint pain warrant professional care.
Difficulty Performing Daily Activities
If joint pain affects your ability to perform daily tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or even dressing, seeking medical advice is recommended.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Joint Health
Maintaining healthy joints involves more than just managing pain—it’s about preventing issues and promoting overall joint well-being. Making certain lifestyle adjustments can help reduce joint strain, improve mobility, and support long-term joint health. Here are some key changes you can incorporate into your daily routine:
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the most effective ways to support joint health and reduce the risk of joint-related issues. Excess body weight puts added stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees, hips, and ankles, which can accelerate wear and tear and lead to conditions like osteoarthritis. Here’s why maintaining a healthy weight is crucial:
Reduces Joint Strain
Each pound of excess weight increases the pressure on your joints, especially those responsible for supporting body weight. For example, every pound gained places additional stress on the knees, making them more prone to discomfort, inflammation, and damage.
Supports Cartilage Health
Healthy cartilage acts as a cushion in your joints, absorbing shock and reducing friction. Excess weight accelerates the breakdown of cartilage, which can lead to joint degeneration and arthritis.
Improves Mobility
Weight management helps maintain flexibility and reduces stiffness in the joints, allowing for better mobility and ease of movement. Losing even a small amount of weight can make a noticeable difference in joint function.
Prevents Complications
Carrying excess weight increases the risk of developing joint conditions such as osteoarthritis, gout, and bursitis. Maintaining a healthy weight minimizes the risk of these complications, promoting long-term joint health.
Enhances Physical Activity
Being at a healthy weight allows for more comfortable physical activities without placing excessive strain on the joints. This supports both cardiovascular health and joint health through regular, low-impact exercise.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on nutrient-dense foods, including whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables.
- Portion Control: Monitor portion sizes to avoid overeating.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling to stay active without putting excess strain on joints.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration helps maintain joint lubrication.
- Seek Support: Consulting a healthcare professional or nutritionist can provide guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Regular Low-Impact Exercise
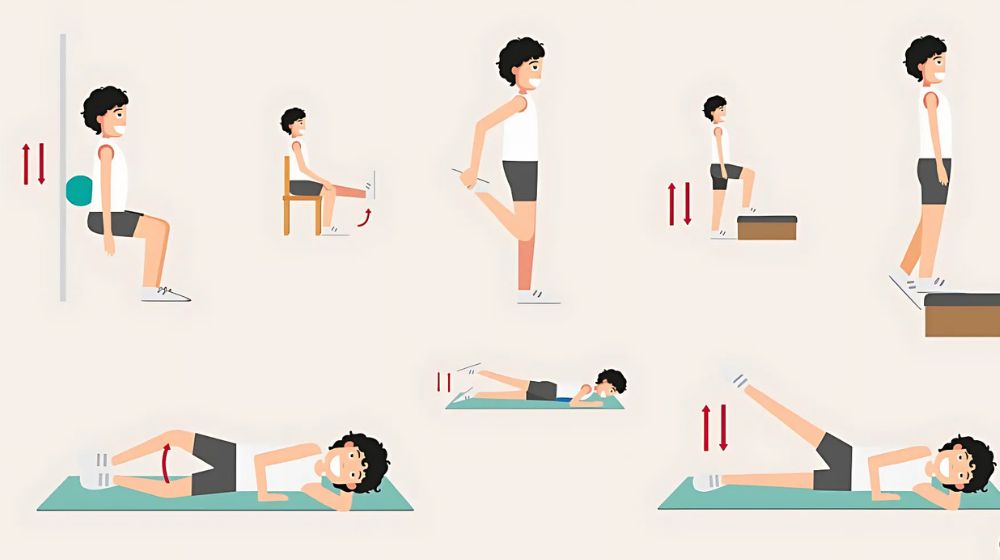
Regular low-impact exercise is essential for maintaining joint health and mobility. Unlike high-impact activities that put excessive strain on joints, low-impact exercises provide numerous benefits without risking joint injury or further deterioration. Here’s why incorporating low-impact exercise into your routine is beneficial:
Benefits of Low-Impact Exercise for Joint Health:
- Reduces Joint Stress
Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, cycling, and yoga, minimize stress on joints compared to high-impact activities like running or jumping. This helps prevent further wear and tear on cartilage and surrounding tissues. - Improves Flexibility and Range of Motion
Gentle movements in low-impact exercises help maintain and improve flexibility, which is essential for healthy joint function. Increased flexibility reduces stiffness and enhances the ability to perform daily activities with ease. - Strengthens Surrounding Muscles
Building muscle around joints provides additional support, reducing the strain placed directly on the joints. Strong muscles help protect the integrity of joints during movement. - Lubricates Joints
Low-impact activities stimulate synovial fluid production, which acts as a natural lubricant for the joints, reducing friction and maintaining smooth movement. - Minimizes Risk of Injury
Since low-impact exercises involve movements that are gentle on joints, they are less likely to cause injuries such as strains, sprains, or joint instability. - Enhances Overall Physical and Mental Well-being
Regular exercise improves overall physical health, reduces inflammation, and helps manage chronic pain. Additionally, activities like yoga or swimming can improve mental well-being by reducing stress and enhancing relaxation.
Examples of Low-Impact Exercises:
- Walking: A simple, accessible way to get moving without straining joints.
- Swimming: Provides a full-body workout while being gentle on joints.
- Cycling: Offers cardiovascular benefits while protecting the knees and hips.
- Yoga: Focuses on flexibility, balance, and joint mobility through gentle stretches and postures.
- Tai Chi: Combines slow, controlled movements with balance and relaxation techniques, promoting joint health.
Proper Nutrition for Joint Health
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining healthy joints and preventing joint-related issues. A well-balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients to support joint function, reduce inflammation, and promote optimal cartilage health. Here’s how proper nutrition can benefit your joints:
Key Nutrients for Joint Health:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, omega-3s help reduce inflammation in joints and may slow the progression of conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin C is essential for the production of collagen, a key component of cartilage. Citrus fruits, bell peppers, and berries are rich sources of vitamin C.
- Vitamin D and Calcium
- These nutrients are important for bone health and joint support. Dairy products, fortified plant-based milk, and leafy greens are good sources of both.
- Antioxidants
- Antioxidants such as vitamin E, found in nuts and seeds, combat oxidative stress, which contributes to joint inflammation and damage.
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin
- These compounds are naturally present in cartilage and are often supplemented for joint health. Foods like shellfish, bone broth, and supplements containing glucosamine and chondroitin can support joint tissue health.
- Fiber and Phytonutrients
- A diet high in fiber and plant-based foods, like whole grains, legumes, and colorful vegetables, provides anti-inflammatory benefits that may improve joint function.
- Curcumin
- Found in turmeric, curcumin has strong anti-inflammatory properties and may help alleviate joint pain associated with conditions like arthritis.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet Tips for Joint Health:
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce intake of sugary snacks, refined carbohydrates, and processed foods, as they can contribute to inflammation.
- Increase Whole Foods: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports synovial fluid production, which helps keep joints lubricated.
- Moderation of Saturated Fats: While some fats are beneficial, excessive saturated fats found in fried or high-fat animal products can promote inflammation.
Here’s a chart summarizing key nutrients and foods for joint health:
| Nutrient | Foods Rich in Nutrient | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds | Reduces inflammation and supports cartilage health |
| Vitamin C | Citrus fruits, bell peppers, berries | Supports collagen production, aiding in healthy cartilage |
| Vitamin D & Calcium | Dairy, fortified plant-based milk, leafy greens | Promotes bone health and joint support |
| Antioxidants | Nuts, seeds, berries, dark leafy greens | Combat oxidative stress and inflammation |
| Glucosamine & Chondroitin | Shellfish, bone broth, supplements | Supports joint tissue health and reduces cartilage breakdown |
| Curcumin | Turmeric, curry spices | Alleviates joint pain and inflammation |
| Fiber & Phytonutrients | Whole grains, legumes, colorful vegetables | Reduces inflammation and promotes overall joint health |
Effective Pain Relief Strategies
Managing joint pain requires a combination of approaches to reduce discomfort, improve mobility, and promote overall joint health. Here are some effective strategies for relieving joint pain:

Medications
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Pain Relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or aspirin can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Topical Treatments: Creams, gels, or patches with ingredients such as menthol, capsaicin, or lidocaine can provide localized relief.
- Prescription Medications: For more severe or chronic pain, your doctor may recommend stronger medications or corticosteroids.
Physical Therapy
- A physical therapist can create a customized exercise program to improve joint strength, flexibility, and mobility while minimizing pain.
- Targeted exercises focus on stabilizing muscles around affected joints, reducing strain and discomfort.
Heat and Cold Therapy
- Heat Therapy: Warm compresses, heating pads, or warm baths help relax muscles and improve blood flow to painful joints.
- Cold Therapy: Ice packs or cold wraps reduce inflammation and numb pain by constricting blood vessels.
Low-Impact Exercise
- Regular low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or yoga help maintain joint health without putting excessive strain on them.
- Strengthening muscles surrounding joints reduces the load placed on them, promoting better function.
Weight Management
- Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips, alleviating pain and promoting long-term joint health.
Proper Nutrition
- Eating anti-inflammatory foods, such as fatty fish, whole grains, and fruits, can help reduce joint inflammation and pain.
- Supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, glucosamine, or turmeric may support joint health and reduce discomfort.
Posture and Ergonomics
- Maintaining good posture and using ergonomic tools or work setups reduces strain on joints during daily activities.
- Proper ergonomics minimize repetitive stress and prevent injury.
Stress Management
- Stress-relief techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or gentle stretching can reduce muscle tension and joint discomfort associated with stress.
Professional Treatment Options
- In cases of severe or persistent joint pain, treatments like cortisone injections, viscosupplementation, or physical therapy can be considered.
- Surgery may be an option for advanced joint damage where less invasive methods are no longer effective.
Natural Remedies and Alternatives
For those seeking alternatives to conventional treatments, several natural remedies can help manage joint pain and improve overall joint health. These remedies often focus on reducing inflammation, promoting healing, and improving mobility. Here are some popular natural options:
Turmeric and Curcumin
- Turmeric contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound that may reduce joint pain and stiffness.
- Adding turmeric to your diet (in smoothies, teas, or supplements) can help alleviate discomfort associated with arthritis and other joint-related issues.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Omega-3s found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts help reduce inflammation, which can ease joint pain and improve joint function.
- Omega-3 supplements may also be used to support joint health, especially in cases of chronic inflammation.
Ginger
- Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, ginger can help reduce swelling and discomfort in joints.
- Consuming fresh ginger root or drinking ginger tea can provide relief for joint pain.
Epsom Salt Baths
- Epsom salt contains magnesium, which can help reduce muscle tension and inflammation, promoting relaxation and joint comfort.
- Soaking in an Epsom salt bath for 20-30 minutes can relieve joint stiffness and promote healing.
CBD (Cannabidiol)
- CBD oil has been found to have anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties, making it a popular natural remedy for joint discomfort.
- Topical creams or oral supplements may help reduce pain and improve joint function, though it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper guidance.
Boswellia (Indian Frankincense)
- Boswellia contains compounds that help reduce inflammation and improve mobility in joints, especially for conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Supplements or extracts are commonly used to manage joint pain.
Essential Oils
- Essential oils like peppermint, eucalyptus, and lavender have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties that can relieve joint pain.
- Massaging diluted essential oils into affected areas may promote circulation and reduce discomfort.
Chiropractic Care and Acupuncture
- Chiropractic adjustments and acupuncture focus on balancing the body’s energy flow and alignment, which may reduce joint pain and improve mobility.
- These holistic approaches aim to treat both the symptoms and underlying causes of joint discomfort.
Dietary Supplements
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: These supplements help rebuild cartilage and improve joint lubrication.
- MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane): Often used alongside glucosamine, MSM has anti-inflammatory properties that support joint health.
Aloe Vera
- Aloe vera gel or juice has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce joint pain and stiffness when applied topically or consumed.
Acai Berries and Chia Seeds
- Rich in antioxidants and omega-3s, these superfoods can help combat inflammation and improve joint health.
Heat and Cold Therapy
- Combining hot and cold therapy is a natural way to manage joint pain by reducing inflammation and promoting circulation.
Joint-Friendly Daily Habits
Maintaining healthy joints requires consistent effort and thoughtful habits that promote joint health, reduce strain, and improve mobility. Incorporating these joint-friendly habits into your daily routine can help manage pain, prevent discomfort, and support long-term joint well-being.
Stay Active with Low-Impact Exercises
- Engage in regular low-impact activities like walking, swimming, cycling, or yoga to keep joints flexible and strong without excessive strain.
- Avoid high-impact activities that can stress joints, such as running or intense jumping exercises.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Excess weight puts added pressure on joints, especially weight-bearing joints like knees and hips. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce joint stress and improve mobility.
Practice Good Posture and Ergonomics
- Maintain proper posture while sitting, standing, or performing daily tasks to reduce unnecessary strain on joints.
- Use ergonomic furniture or setups when working at a desk or engaging in physical activities to avoid joint misalignment or overuse.
Incorporate Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
- Regular stretching and strengthening exercises help maintain joint flexibility and stability.
- Focus on exercises that target muscles surrounding the joints, promoting better support and reducing joint wear and tear.
Prioritize Rest and Recovery
- Allow time for joint recovery by incorporating rest days between activities. Overuse can lead to joint inflammation and discomfort.
- Apply ice or heat therapy to sore joints as needed for pain relief and improved recovery.
Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet
- Consume foods rich in anti-inflammatory nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins C and D, and antioxidants to support joint health.
- Limit processed and inflammatory foods that may exacerbate joint discomfort.
Stay Hydrated
- Proper hydration is essential for joint health, as it helps maintain synovial fluid—the natural lubricant for joints.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to ensure optimal joint function.
Practice Stress Management
- Chronic stress can lead to inflammation, which may negatively impact joint health. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, and gentle exercises like tai chi can help manage stress and improve joint well-being.
Limit Repetitive Movements
- Avoid prolonged repetitive motions that strain joints, such as lifting heavy objects or performing the same task repeatedly.
- Take breaks and incorporate variations in activities to reduce joint strain.
10. Regular Medical Check-Ups
- Routine visits to a healthcare professional can help monitor joint health, detect early signs of joint issues, and ensure proper treatment if needed.
Conclusion
Managing joint pain and maintaining joint health involves a combination of proactive habits, proper nutrition, regular exercise, and mindful lifestyle choices. Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce stress on weight-bearing joints, alleviating pain and promoting better joint function. Incorporating low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and yoga can improve joint flexibility, strength, and overall mobility while minimizing the risk of injury. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals supports healthy cartilage and reduces joint discomfort. Practicing joint-friendly habits like maintaining good posture, limiting repetitive movements, and ensuring sufficient rest can prevent joint strain and enhance mobility. Additionally, natural remedies such as turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 supplements may provide further relief from joint pain and inflammation.
FAQs About Joint Pain Relief
What causes joint pain?
Joint pain can result from arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis), injuries, overuse, gout, infections, or conditions like lupus or fibromyalgia.
What are the most common types of arthritis that cause joint pain?
Osteoarthritis (wear and tear of cartilage) and rheumatoid arthritis (an autoimmune condition) are the most common forms.
How can I relieve joint pain at home?
Home remedies include rest, ice/heat therapy, over-the-counter pain relievers (like ibuprofen), stretching exercises, and using joint braces or supports.
Are there specific foods that help with joint pain?
Yes, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, walnuts), antioxidants (berries, spinach), and anti-inflammatory compounds (turmeric, ginger) may reduce joint pain.
Can weight loss help reduce joint pain?
Absolutely. Losing excess weight reduces the stress on weight-bearing joints like knees and hips, improving pain and mobility.
What are the best exercises for joint pain?
Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, yoga, and walking can strengthen muscles and improve joint function without overloading the joints.
Should I avoid exercise if I have joint pain?
No. Gentle exercises help maintain joint flexibility and strength. However, avoid activities that exacerbate pain or cause swelling.
When should I see a doctor for joint pain?
Seek medical attention if joint pain persists for more than a few weeks, worsens, is accompanied by swelling or redness, or interferes with daily activities.
Are there supplements that help with joint pain?
Supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin, omega-3 fatty acids, and turmeric (curcumin) may support joint health, but consult a doctor before starting them.
Can stress worsen joint pain?
Yes. Stress can increase inflammation and muscle tension, potentially worsening joint pain.
Is heat or cold therapy better for joint pain?
Cold therapy is better for reducing inflammation and swelling, while heat therapy is effective for soothing stiff joints and improving blood flow.
Are there natural remedies for joint pain relief?
Yes, natural options include turmeric, ginger, Epsom salt baths, essential oils (like eucalyptus or lavender), and acupuncture.
What medications are available for joint pain relief?
Common medications include over-the-counter NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen), acetaminophen, corticosteroids, and disease-modifying drugs for arthritis.
How do I prevent joint pain as I age?
Maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, avoid overuse injuries, eat a balanced diet, and use proper posture and ergonomics.
Can joint pain be cured?
While some causes (e.g., injuries or infections) are treatable, chronic conditions like arthritis often require long-term management rather than a cure.
By healthylyfe